Background and general introduction¶
What’s in a name?¶
In the American English term “Computer Science”, the emphasis is on the computer, from its architecture all the way to its use (i.e., on Aristotle’s formal cause). However, as Edsger Dijkstra allegedly put it once, Computer Science is no more [only] about computers than astronomy is [only] about telescopes, and indeed one often sees the term “Computing Science” instead, where the emphasis is on the processing of data on computers (i.e., on Aristotle’s efficient cause). In Denmark, Peter Naur proposed the terms “datalogi” and “Data Science”, where the emphasis is on the representation of information as data on computers for processing (i.e., on Aristotle’s material cause). In Germany, Karl Steinbuch proposed the term “informatik” in 1956, and in France, Philippe Dreyfus proposed the term “informatique” in 1962, terms that are rendered in English as “informatics”, where the emphasis is on the automated treatment of information by processing data on computers (i.e., on Aristotle’s final cause).
To sum up, data are representations of information in a computer, and these representations are processed to carry out a computation. And while the term “Computer Science” is the accepted one, alternative terms exist. For example,
- the National University of Singapore has a School of Computing and the University of Oxford had a Computing Laboratory,
- the University of Edinburgh has a School of Informatics and the Technical University of Denmark has a Department of Informatics,
- Acta Informatica and Fundamenta Informaticae are two peer-reviewed journals in theoretical computer science,
- the “C” in “ACM” stands for “Computing”,
- the “D” in “DIKU”, at the University of Copenhagen, stands for “Datalogi”,
- the closing “I” and “A” in “INRIA” respectively stand for “Informatique” and (translated into English:) “Automation”, and
- the “C” in the MCS major at Yale-NUS College stands for “Computation”.
Information and data¶
Data represent information and is built using data constructors:
- A representation is sound when using constructors correctly always yields a piece of data that correctly represents the information it is meant to represent. (Otherwise this representation is unsound.)
- A representation is complete when all the information we wish to represent can be represented using the data constructors. (Otherwise this representation is incomplete.)
For example, in OCaml (the programming language of discourse for Intro to CS), the default representation of integers has a fixed size, and so only integers between, e.g., -4611686018427387904 and 4611686018427387903 can be represented. This representation is sound in that the representation of any integer between -4611686018427387904 and 4611686018427387903 does correspond to a mathematical integer, but it is incomplete since integers smaller than -4611686018427387904 or greater than 4611686018427387903 cannot be represented.
For another example, in Chez Scheme, the default representation of integer does not have a fixed size: this representation is complete... modulo the size of the memory of our computer.
Epistemology of representation¶
In a nutshell, the representation is separate from what is represented:
- a name is not what it denotes (e.g., we are not our name);
- the address of one’s home is not one’s home;
- a music note is not its name (e.g., because they have several names: do, ré, mi, fa, sol, etc. or A, B, C, D, etc.);
- etc.
Harald: So a number is not its name?Mimer: Right. A number is not its name.Harald: So much for the multiplication tables.Mimer (surprised): The multiplication tables?Harald: Yes. We had to learn them by heart.Mimer: Well, they are still valid any way we look at them.Harald: Yes, but suddenly they are less simple.Mimer: Why? They also work in another language than the one you grew up with.Harald: Harrumph.
Several of René Magritte‘s paintings illustrate this point, e.g., The Treachery of Images where the painting of a pipe is accompanied by the words “Ceci n’est pas une pipe” (“This is not a pipe”), a point Walter Jon Williams developed eloquently in his novel This is not a game.
Computing as data processing¶
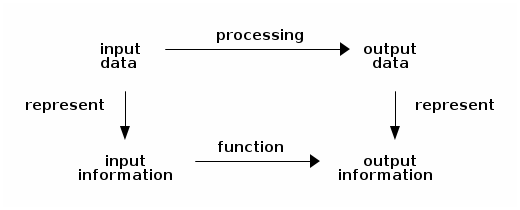
A computer processes data. Given some input data that represent input information, it can:
- yield output data, which represent new information,
- issue an error message (which is also a piece of output data), or
- loop, i.e., not produce any output data.
In so doing, the computer carries out a computation:
Programs¶
A program is the recipe the computer executes to process data: a program computes a function from input information to output information.
Programming languages¶
A programming language is the language in which a program is written: a notation to express computations. There are many notions of computation (i.e., ways of representing information and ways of processing data), and for each of these notions, there are many notations (i.e., many programming languages).
What we need are notions, not notations.—Carl-Friedrich Gauss (quoted by Paul Lockhart in his Mathematician’s Lament)
Postlude¶
Loki: It would indeed be nonsensical to refer to Astronomy as “Telescope Science”.
Mimer: Glad you agree.
Loki: By the token above, at the beginning of this lecture note, Astronomy should be referred to as “Telescoping Science”.
Mimer (who didn’t see this one coming): Telescoping Science.
Loki: Or better, on the ground that Computer Science is about data (cf. Data Science), Astronomy should be called Star Science, based on its etymology.
Mimer (recovering): You know what, Loki, you are right. And by that logic, top astronomers would be nominated to the Star Academy. It would make so much more science, I mean sense.
Loki: Glad you agree. Next step: meteorology, the science of meteors.